

Streaming using the GUI is only available on the Qt interface. Running "vlc" should be all that is needed to open VLC:Ī typical commandline string for converting a file to another format is: On Unix-based system (such as Linux and macOS) a terminal window can be opened. Should change to the directory where vlc.exe is located. If VLC is installed in the default location (on a 32-bit system) running:
#Change default program on mac for mp3 .exe#
exe part is assumed) needs to entered to run VLC. Once the Command Prompt window is opened navigating to the folder/directory where VLC is located is easiest for using the commandline as only "vlc.exe" or "vlc" (as the. Alternatively by going to "Start > Run." or pressing "Windows key + R", entering "cmd" into the text field and press "OK" or Enter. This can be found in the "Accessories" folder of the Start menu. On Windows-based systems the Command Prompt can be used. To use the VLC's commandline you need to have access to the commandline interface, for example via a shell.
#Change default program on mac for mp3 full#
This is more flexible than via the GUI as it enables full usage of the modules and options available in VLC. If the profile settings were compatible and transcoding was successful, a playable destination file should be created.Īnother method of transcoding is via the commandline. To check/edit the settings of a given profile press the "Edit selected profile" button.

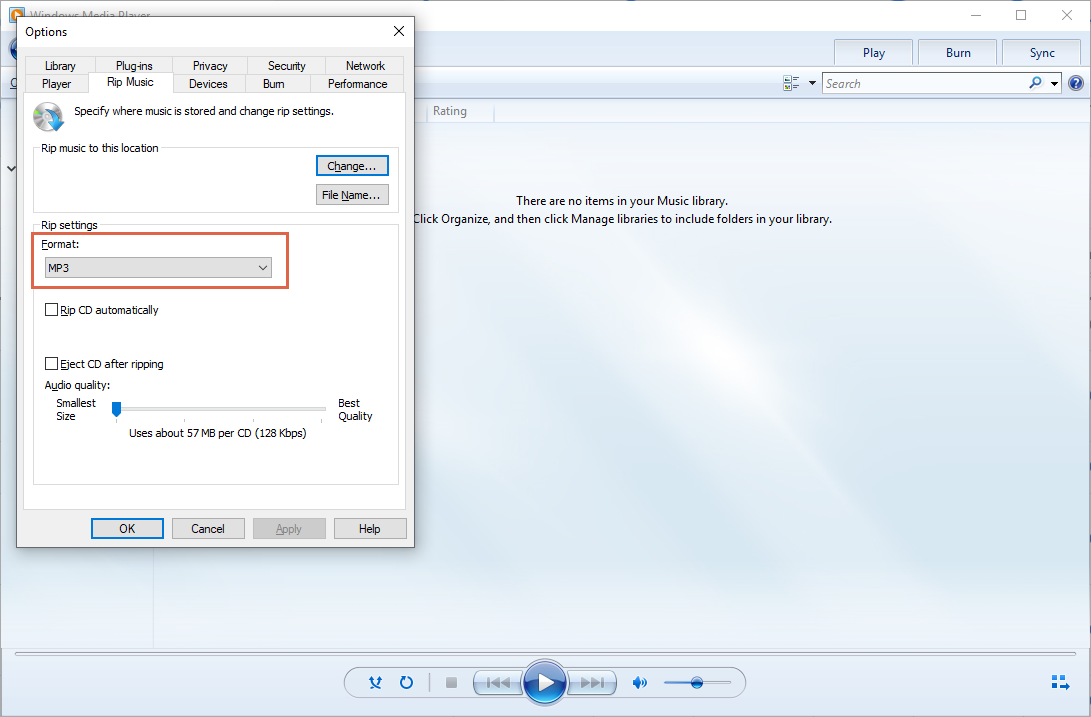
One of the methods of transcoding is via the GUI. The term transcode by itself normally refers to converting one media format to another and saving the output to a file (i.e. There are two methods for transcoding in VLC: via the GUI (VLC's default interface) or via the commandline. Transcoding is the process of taking a media file or stream and converting it to a different format or bitrate. For more information about the formats and codecs supported please see the VideoLAN Streaming Features list. VLC media player is able to stream, transcode and save different media streams.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
